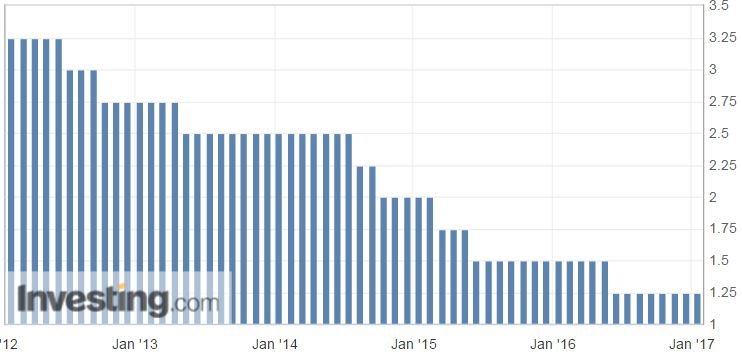
The Bank of Korea (BoK) in its first monetary policy meeting of 2017 left its benchmark interest rate at record low of 1.25 percent, as markets widely expected. The board members defended this decision in the wake of global economic recovery, led by the US and some emerging market economies. Also, diminished global financial market volatility and rise in stock prices supported the central bank’s policy stance.
Looking ahead, the board judges that the global economic recovery will be affected by factors such as the directions of the new US government's economic policies, the pace of monetary policy normalization by the US Federal Reserve, and the movements toward spreading trade protectionism.
The Board sees the domestic economy as likely to continue its trend of moderate growth going forward, and forecasts a rate of GDP growth for this year in the mid-2 percent range. The trend of recovery in domestic demand activities is expected to be limited, due to deteriorations in economic sentiment for example, but exports will likely improve thanks chiefly to the global economic recovery.
Looking ahead the Board forecasts that consumer price inflation will gradually rise to near the 2 percent target level by around the middle of 2017, on the effects mainly of the increases in international oil prices, and that core inflation will maintain a level in the mid- to upper-1 percent range.
Lastly, the policy statement maintained that the central bank board members will conduct monetary policy so as to ensure that the recovery of economic growth continues and consumer price inflation approaches the target level over a medium-term horizon, while paying attention to financial stability.
The central bank in its forecast report said that the real GDP will increase by 2.5 percent in 2017 and by 2.8 percent in 2018. The Korean economy is expected to continue its moderate growth, driven by the improvement in exports and facilities investment thanks to the recovery of the major economies, while the growth in private consumption and construction investment are projected to slow down. In 2018 economic growth is projected to be 2.8 percent, supported by further improvements in exports and facilities investment as the global economy continues to recover.
Headline consumer prices are expected to rise by 1.8 percent in 2017, and by 1.9 percent in 2018. It is forecast that the pace of inflation will accelerate, in line with the higher level of oil prices compared to last year. And for 2018, inflation will increase about 0.1% as domestic economy gradually recovers. The current account balance is forecast to be around 81.0 billion dollars in 2017, and around 78.0 billion dollars in 2018.



 Federal Reserve Faces Subpoena Delay Amid Investigation Into Chair Jerome Powell
Federal Reserve Faces Subpoena Delay Amid Investigation Into Chair Jerome Powell  RBA Raises Interest Rates by 25 Basis Points as Inflation Pressures Persist
RBA Raises Interest Rates by 25 Basis Points as Inflation Pressures Persist  Gold and Silver Prices Climb in Asian Trade as Markets Eye Key U.S. Economic Data
Gold and Silver Prices Climb in Asian Trade as Markets Eye Key U.S. Economic Data  Dollar Near Two-Week High as Stock Rout, AI Concerns and Global Events Drive Market Volatility
Dollar Near Two-Week High as Stock Rout, AI Concerns and Global Events Drive Market Volatility  Trump Signs Executive Order Threatening 25% Tariffs on Countries Trading With Iran
Trump Signs Executive Order Threatening 25% Tariffs on Countries Trading With Iran  Japan Economy Poised for Q4 2025 Growth as Investment and Consumption Hold Firm
Japan Economy Poised for Q4 2025 Growth as Investment and Consumption Hold Firm  ECB’s Cipollone Backs Digital Euro as Europe Pushes for Payment System Independence
ECB’s Cipollone Backs Digital Euro as Europe Pushes for Payment System Independence  South Africa Eyes ECB Repo Lines as Inflation Eases and Rate Cuts Loom
South Africa Eyes ECB Repo Lines as Inflation Eases and Rate Cuts Loom  Trump Lifts 25% Tariff on Indian Goods in Strategic U.S.–India Trade and Energy Deal
Trump Lifts 25% Tariff on Indian Goods in Strategic U.S.–India Trade and Energy Deal  Bank of England Expected to Hold Interest Rates at 3.75% as Inflation Remains Elevated
Bank of England Expected to Hold Interest Rates at 3.75% as Inflation Remains Elevated