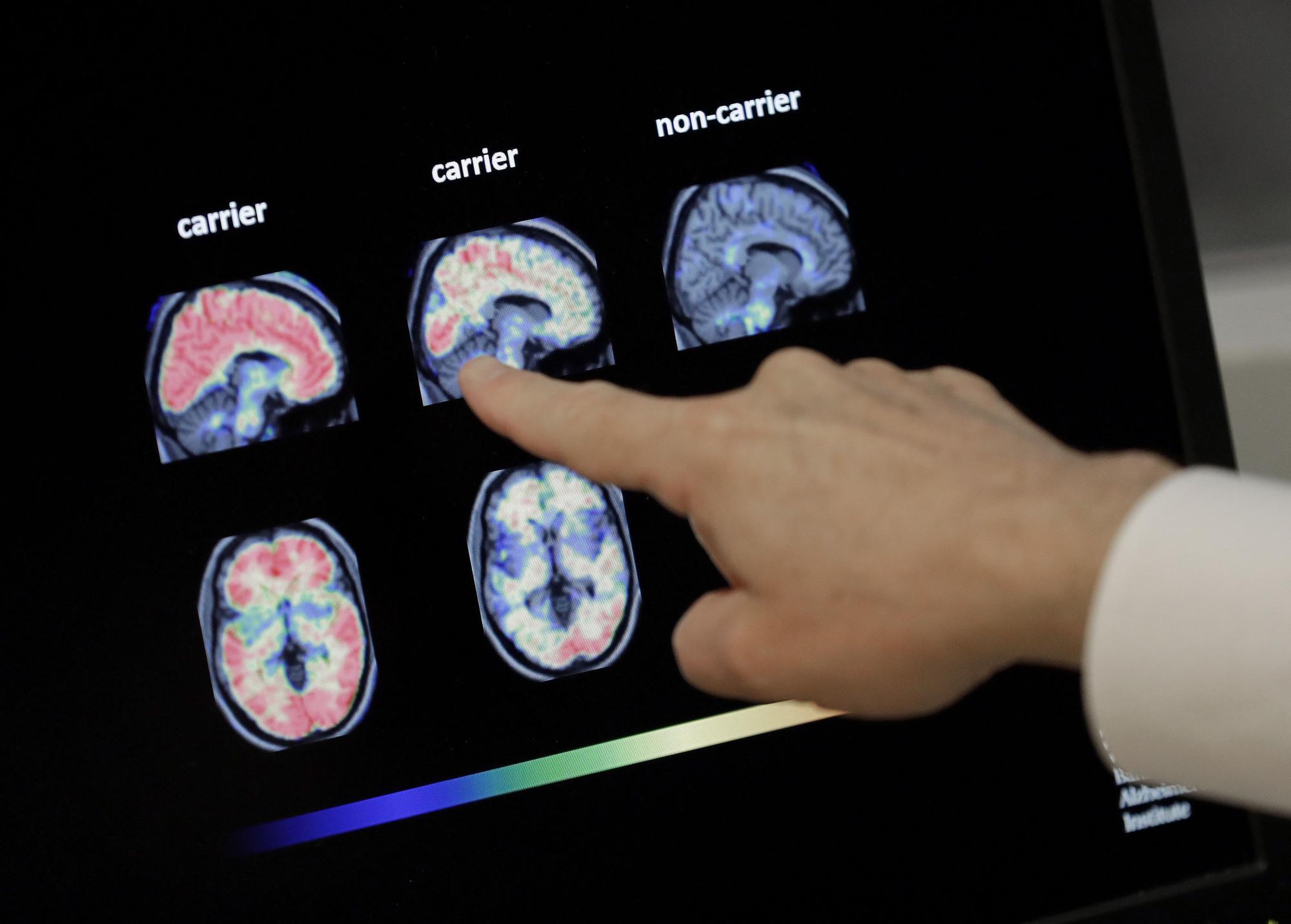
A team of Japanese scientists has developed a method that utilizes glucose and fragmented antibodies in reducing an abnormal accumulation of protein in the brains of mice with Alzheimer’s disease.
According to Takanori Yokota, a neurology professor at the university who was part of the team, they hope accomplishment will lead to the development of a new therapy that is safer and more efficient than its conventional antibody-used counterpart.
The amyloid beta protein accumulation in the brain is believed to trigger Alzheimer’s.
The researchers, primarily from Tokyo Medical and Dental University and the Innovation Center of Nanomedicine (iCONM), encapsulated fragments of an antibody that can attach itself to the protein and remove it from the brain into a so-called nanomachine.
They also attached glucose molecules to the nanomachine's surface, making it simpler for the brain to receive the antibody.
The mice with abnormally high levels of amyloid beta due to the disease were given injections of the encapsulated antibody fragments by the researchers. The agent was administered weekly for 10 weeks.
In contrast to just injecting them there, the study found that employing a nanomachine can deliver 80 times more antibody fragments to the brain.
It was also established that this technique can be used to get rid of amyloid beta lumps, which prevented the protein from gathering.
Because a whole antibody is too large to be placed in many places, the researchers chose to employ antibody fragments instead.
The result was a positive effect that was unanticipated.
Historically, the blood-brain barrier, which determines what to take in from blood vessels to protect the brain, prevented the entire prescribed medication to eliminate the protein from reaching the brain.
Therapeutic antibodies for Alzheimer's disease are well known for having undesirable side effects, such as inflamed brain swelling.
As the fragmented antibody lacks the portion that causes inflammatory reactions, the team anticipates that this side effect may be avoided.



 Trump Signs Executive Order to Boost AI Research in Childhood Cancer
Trump Signs Executive Order to Boost AI Research in Childhood Cancer  CDC Vaccine Review Sparks Controversy Over Thimerosal Study Citation
CDC Vaccine Review Sparks Controversy Over Thimerosal Study Citation  Tencent Shares Slide After WeChat Restricts YuanBao AI Promotional Links
Tencent Shares Slide After WeChat Restricts YuanBao AI Promotional Links  FDA Fast-Track Drug Reviews Delayed Over Safety and Efficacy Concerns
FDA Fast-Track Drug Reviews Delayed Over Safety and Efficacy Concerns  NASA and SpaceX Target Crew-11 Undocking From ISS Amid Medical Concern
NASA and SpaceX Target Crew-11 Undocking From ISS Amid Medical Concern  Novo Nordisk Warns of Profit Decline as Wegovy Faces U.S. Price Pressure and Rising Competition
Novo Nordisk Warns of Profit Decline as Wegovy Faces U.S. Price Pressure and Rising Competition  OpenAI Expands Enterprise AI Strategy With Major Hiring Push Ahead of New Business Offering
OpenAI Expands Enterprise AI Strategy With Major Hiring Push Ahead of New Business Offering  Russian Stocks End Mixed as MOEX Index Closes Flat Amid Commodity Strength
Russian Stocks End Mixed as MOEX Index Closes Flat Amid Commodity Strength  Cogent Biosciences Soars 120% on Breakthrough Phase 3 Results for Bezuclastinib in GIST Treatment
Cogent Biosciences Soars 120% on Breakthrough Phase 3 Results for Bezuclastinib in GIST Treatment  U.S. Stock Futures Slide as Tech Rout Deepens on Amazon Capex Shock
U.S. Stock Futures Slide as Tech Rout Deepens on Amazon Capex Shock  SoftBank Shares Slide After Arm Earnings Miss Fuels Tech Stock Sell-Off
SoftBank Shares Slide After Arm Earnings Miss Fuels Tech Stock Sell-Off  Gold and Silver Prices Rebound After Volatile Week Triggered by Fed Nomination
Gold and Silver Prices Rebound After Volatile Week Triggered by Fed Nomination  India–U.S. Interim Trade Pact Cuts Auto Tariffs but Leaves Tesla Out
India–U.S. Interim Trade Pact Cuts Auto Tariffs but Leaves Tesla Out  RFK Jr. Overhauls Federal Autism Panel, Sparking Medical Community Backlash
RFK Jr. Overhauls Federal Autism Panel, Sparking Medical Community Backlash