In March, we expect the German trade surplus to have amounted to €21.9bn, up from €19.5bn in February. Exports are expected to have increased by 0.2% MoM, following the rise of 1.4% MoM in February (-2.1%), while imports are expected to have decreased by 0.4% MoM, in line with signs of weak retail sales.
In Europe, Manufacturer's PMI for April that France and Greece produced readings of below 50.0 for the month, demonstrating an accelerated decline in factory production. Germany delivered a final reading of 52.1, Spain and Italy produced readings of 53.8 and 54.2 respectively. Currency traders await a general election on 7th May to elect the 56th Parliament of the United Kingdom.
While export data remain suppressed, temporary weakness in China linked to the New Year and in the US linked to weather and industrial action has probably distorted data temporarily in Q1. The weakening in Q1 exports looks particularly noteworthy in view of the significant weakening of the euro last year.
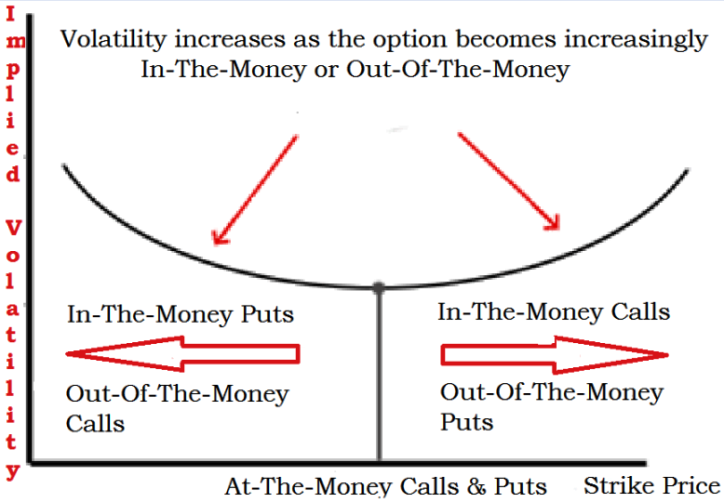
Increasing Implied volatility and Risk Management through currency derivatives:
Futures and Options contracts are highly useful in hedging purpose. But using the concept of Implied Volatility, one can determine whether a certain Call or Put is relatively expensive or cheaper.
Implied Volatility is the current Volatility of the underlying currency implied in its observed Option Price.
Using the Black Scholes formula one can find out the Volatility value that would result in the model producing the Option price which is equal to current market price.
As volatility affects the price of an option contract, an over estimation of volatility will result in overpriced option and an under estimation resulting in underpriced option.
China distorting German exports adding weakness to Euro growth
Tuesday, May 5, 2015 6:47 AM UTC
Editor's Picks
- Market Data
Most Popular



 BTC Flat at $89,300 Despite $1.02B ETF Exodus — Buy the Dip Toward $107K?
BTC Flat at $89,300 Despite $1.02B ETF Exodus — Buy the Dip Toward $107K?  JPMorgan Lifts Gold Price Forecast to $6,300 by End-2026 on Strong Central Bank and Investor Demand
JPMorgan Lifts Gold Price Forecast to $6,300 by End-2026 on Strong Central Bank and Investor Demand 






























