The number of job seekers that dropped out of the Japan's labour force increased in March and April, and these job seekers returned to the labour force in May and June. Most of them were absorbed by the increase in employment numbers.
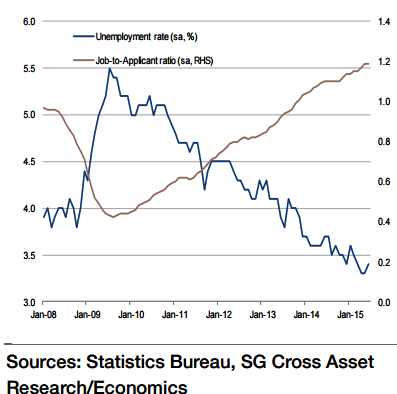
"The Japan unemployment rate is expected to remain unchanged at 3.4% in July. Both the manufacturing and non-manufacturing sectors are feeling the labour shortage and are stepping up hiring. The unemployment rate is expected to continue to remain below 3.5%, corresponding to the NAIRU level. This in turn should underpin sentiment just as aggregate wages start to expand, thus enabling Japan to make a full exit from deflation", says Societe Generale.
However, if this situation fails to materialise, the BoJ's 2% price stability target will be difficult to achieve. The unemployment rate needs to fall below 3% for the target to be met, but this level currently seems very far away.
"The job-to-applicant ratio is likely to rise further to 1.20 in June from 1.19 in June. This is the highest level since 1992 and indicates that companies remain willing to increase their hiring", added Societe Generale.
Japan's July unemployment rate likely to be unchanged at 3.4%
Thursday, August 27, 2015 5:44 AM UTC
Editor's Picks
- Market Data
Most Popular



 Oil Tanker Attacks in Gulf Escalate U.S.–Iran Conflict, Driving Energy Prices Higher
Oil Tanker Attacks in Gulf Escalate U.S.–Iran Conflict, Driving Energy Prices Higher  Australia and Canada Strengthen Critical Minerals Partnership Through New G7 Alliance Agreements
Australia and Canada Strengthen Critical Minerals Partnership Through New G7 Alliance Agreements  Gold Prices Steady in Asian Trade as Strong Dollar and Rising Yields Weigh on Bullion
Gold Prices Steady in Asian Trade as Strong Dollar and Rising Yields Weigh on Bullion  KOSPI Plunges Over 8% as U.S.-Iran War Sparks Global Risk Aversion and Profit-Taking
KOSPI Plunges Over 8% as U.S.-Iran War Sparks Global Risk Aversion and Profit-Taking  U.S. Stocks Rise as Strong Economic Data Offsets Middle East Conflict Concerns
U.S. Stocks Rise as Strong Economic Data Offsets Middle East Conflict Concerns  China Sets 2026 Growth Target at 4.5–5% While Prioritizing Innovation and Industrial Strength
China Sets 2026 Growth Target at 4.5–5% While Prioritizing Innovation and Industrial Strength  Trump Offers U.S. Insurance and Naval Escort for Tankers as Strait of Hormuz Crisis Disrupts Global Oil Trade
Trump Offers U.S. Insurance and Naval Escort for Tankers as Strait of Hormuz Crisis Disrupts Global Oil Trade  Chinese Yuan Edges Higher but Faces Biggest Weekly Drop in Over a Year Amid Strong Dollar
Chinese Yuan Edges Higher but Faces Biggest Weekly Drop in Over a Year Amid Strong Dollar 






























