Announcement of CRR Cut
On December 6, 2024, the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) announced a cut in the Cash Reserve Ratio (CRR) by 50 basis points (bps), lowering it from 4.5% to 4%. This is the first time the CRR has been reduced since March 2020. The move aims to increase cash flow in the banking system, which has been tight due to high foreign exchange interventions and a recent drop in GDP growth to 5.4% for the July-September quarter.
Impact on Bank Liquidity
The CRR cut is expected to free up around ₹1.1 lakh crore to ₹1.2 lakh crore in bank liquidity, enabling banks to lend more money and support economic growth. The RBI is signaling a desire to ease monetary policy without changing the repo rate, which remains at 6.5%. This decision comes even as inflation has risen to 6.2% in October, exceeding the central bank's acceptable limit.
Economists say that this CRR cut could help banks lower interest rates for borrowers, which may encourage spending and investment in a tough economic situation with low growth and inflation concerns. The RBI is trying to balance supporting economic growth while controlling inflation as it deals with these complex challenges
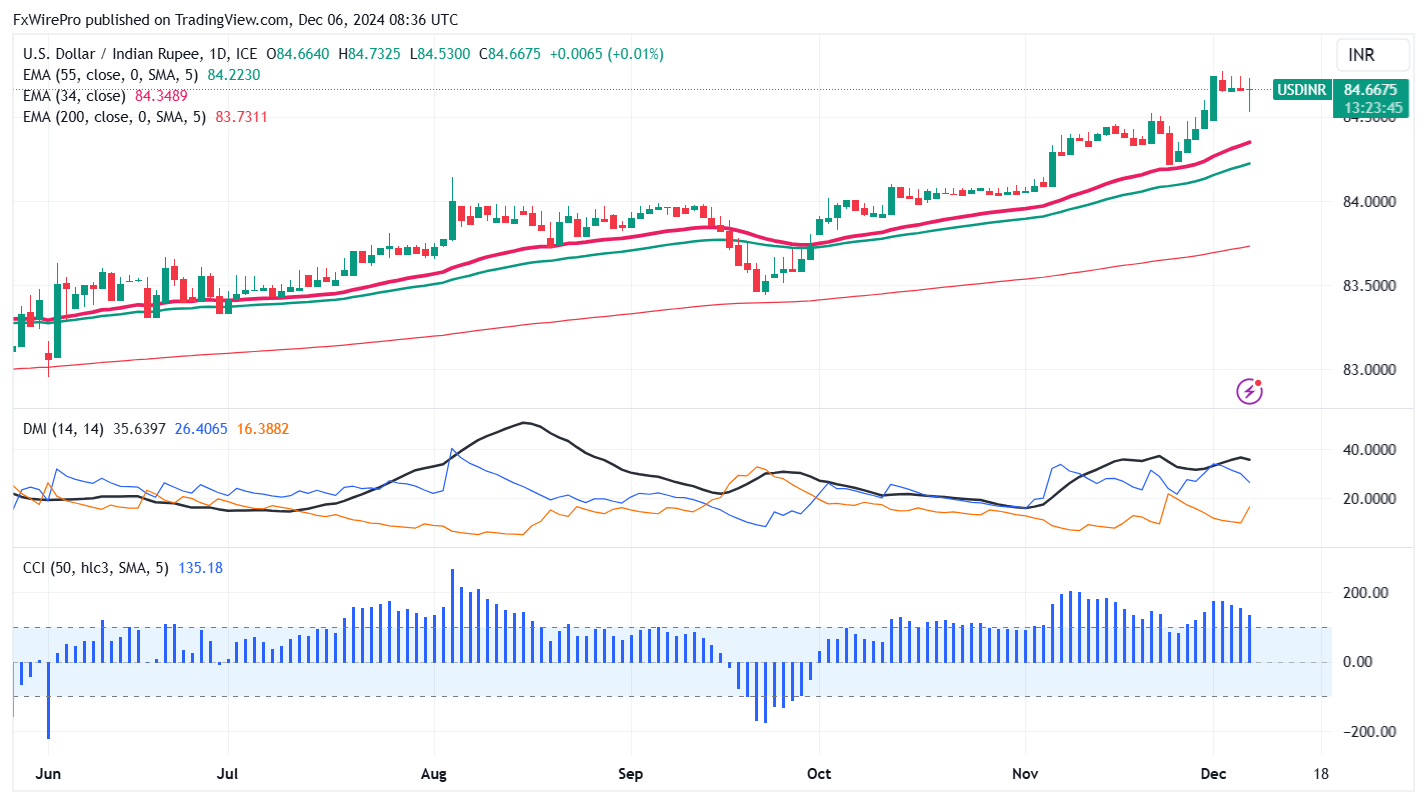
Technicals-
Major resistance- 85
Near-term resistance - 84.80
Minor support- 84.20/83.60, 83.25
Trend reversal level- 83



 China Extends Gold Buying Streak as Reserves Surge Despite Volatile Prices
China Extends Gold Buying Streak as Reserves Surge Despite Volatile Prices  South Africa Eyes ECB Repo Lines as Inflation Eases and Rate Cuts Loom
South Africa Eyes ECB Repo Lines as Inflation Eases and Rate Cuts Loom  Elon Musk’s Empire: SpaceX, Tesla, and xAI Merger Talks Spark Investor Debate
Elon Musk’s Empire: SpaceX, Tesla, and xAI Merger Talks Spark Investor Debate  RBA Expected to Raise Interest Rates by 25 Basis Points in February, ANZ Forecast Says
RBA Expected to Raise Interest Rates by 25 Basis Points in February, ANZ Forecast Says  BOJ Rate Decision in Focus as Yen Weakness and Inflation Shape Market Outlook
BOJ Rate Decision in Focus as Yen Weakness and Inflation Shape Market Outlook  Fed Governor Lisa Cook Warns Inflation Risks Remain as Rates Stay Steady
Fed Governor Lisa Cook Warns Inflation Risks Remain as Rates Stay Steady