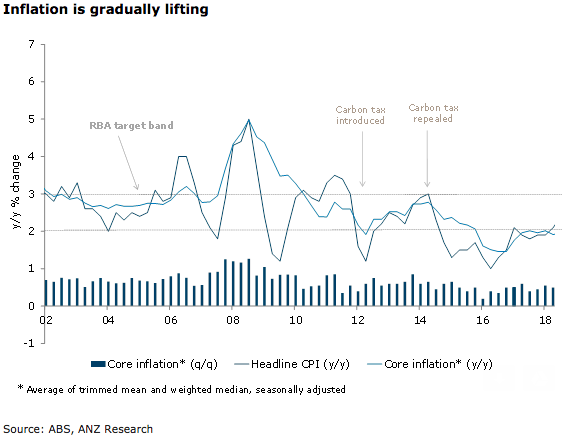
Australia’s consumer price inflation for the second quarter of this year slightly beat market expectations, confirming that inflationary pressures are building only very gradually. From a policy perspective, the Q2 data supports the case that the Reserve Bank of Australia (RBA) is a long way from policy tightening.
Headline CPI rose 0.4 percent q/q, a little below expectations of 0.5 percent q/q. This was still sufficient to push annual inflation higher, to 2.1 percent y/y from 1.9 percent y/y in the first quarter. As expected, petrol prices contributed 0.2 ppt of the rise.
Both the trimmed mean and weighted median rose by 0.5 percent q/q, in line with expectations, leaving annual core inflation running a touch below the central bank’s target band. Looking in more detail, the average of the two measures rose 0.46% q/q, a step-down from 0.54% in Q1. CPI ex volatiles (seasonally adjusted) rose 0.47 percent q/q. In annual terms, core inflation decelerated a touch, to 1.9 percent y/y, from (an upwardly revised) 2.0 percent y/y in Q1.
Further, tradable prices were boosted by the 6.9 percent rise in petrol prices in Q1, excluding volatiles and tobacco tradable prices, seasonally adjusted, fell by 0.5 percent q/q, down 2.6 percent y/y. Retail competition is still impacting, with prices lower over the year for clothing & footwear (-2.0 percent), furniture & furnishings (-2.1 percent) and household appliances (-1.6 percent).
"In our view, inflation will rise only very gradually, with sufficient progress toward the mid-point of the policy target band unlikely to emerge until H2 2019. Higher inflation will require a lift in wage growth feeding through to domestic services prices. Focus will now turn to the Q2 Wage price Index on August 15," ANZ Research commented in its latest report.



 Oil Prices Slide on US-Iran Talks, Dollar Strength and Profit-Taking Pressure
Oil Prices Slide on US-Iran Talks, Dollar Strength and Profit-Taking Pressure  Bank of Japan Signals Readiness for Near-Term Rate Hike as Inflation Nears Target
Bank of Japan Signals Readiness for Near-Term Rate Hike as Inflation Nears Target  Vietnam’s Trade Surplus With US Jumps as Exports Surge and China Imports Hit Record
Vietnam’s Trade Surplus With US Jumps as Exports Surge and China Imports Hit Record  Best Gold Stocks to Buy Now: AABB, GOLD, GDX
Best Gold Stocks to Buy Now: AABB, GOLD, GDX  Gold Prices Fall Amid Rate Jitters; Copper Steady as China Stimulus Eyed
Gold Prices Fall Amid Rate Jitters; Copper Steady as China Stimulus Eyed  Fed Confirms Rate Meeting Schedule Despite Severe Winter Storm in Washington D.C.
Fed Confirms Rate Meeting Schedule Despite Severe Winter Storm in Washington D.C.  Global Markets Slide as AI, Crypto, and Precious Metals Face Heightened Volatility
Global Markets Slide as AI, Crypto, and Precious Metals Face Heightened Volatility