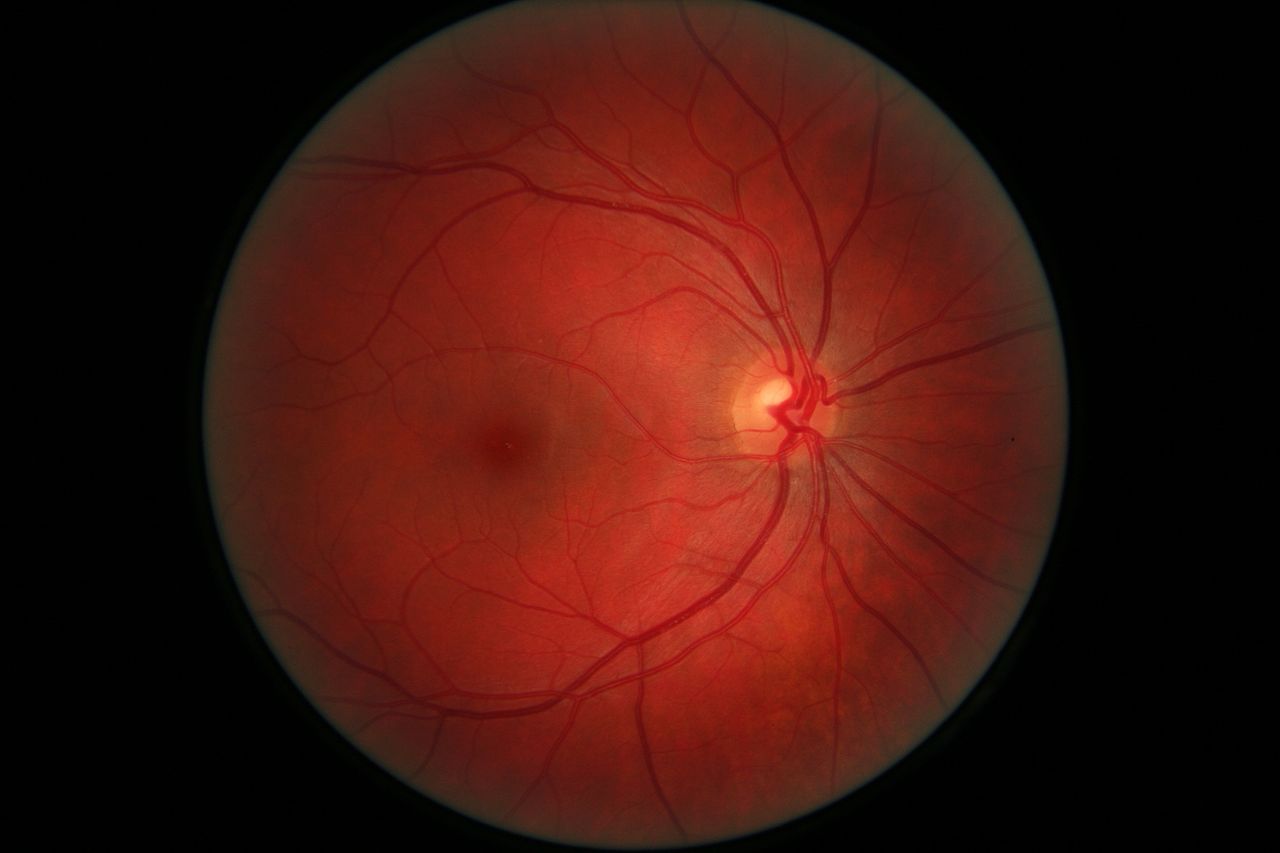
It would seem that the time when machines surpass the ability of humans to do intricate work is almost here. One of Google’s Artificial Intelligence projects is apparently capable of diagnosing the retina of patients to see if they are about to go blind. The search engine company even went so far as to claim that the AI is better than actual doctors at diagnosis.
As Google noted in a blog post about the AI, Diabetic retinopathy is a quickly rising cause of blindness among patients in the world. The disease is treatable, but only if it is caught early enough to respond to treatments. This is where effective diagnosis comes into play.
“Unfortunately, medical specialists capable of detecting the disease are not available in many parts of the world where diabetes is prevalent,” the blog post reads. “We believe that Machine Learning can help doctors identify patients in need, particularly among underserved populations.”
The findings with regards to the diagnostic capabilities of the AI was published in the Journal of the American Medical Association. The paper included proposals on certain potential benefits that machine learning could provide with regards to diagnosing medical problems and even helping to find ways to treat them.
In the case of blindness caused by Diabetic retinopathy, the AI is fed images of retinas, which it will then scan and analyze for any of the telltale sign of impending blindness. After going through 128,000 images of retinas with the traits that led to the condition, the AI was given 10,000 new images to diagnose. Based on the results, the machine was much better at detecting which images posed the biggest threat of blindness for the subjects.
There are significant advantages to having this kind of powerful tool, especially with regards to detecting and curing diseases. However, there is also the startling implication that if a machine can replace vocations as complex and important as those in the medical profession, just how much of human society can AI replace?



 FDA Fast-Tracks Approval of Altria’s on! PLUS Nicotine Pouches Under New Pilot Program
FDA Fast-Tracks Approval of Altria’s on! PLUS Nicotine Pouches Under New Pilot Program  Baidu Approves $5 Billion Share Buyback and Plans First-Ever Dividend in 2026
Baidu Approves $5 Billion Share Buyback and Plans First-Ever Dividend in 2026  Elon Musk’s Empire: SpaceX, Tesla, and xAI Merger Talks Spark Investor Debate
Elon Musk’s Empire: SpaceX, Tesla, and xAI Merger Talks Spark Investor Debate  Elon Musk’s SpaceX Acquires xAI in Historic Deal Uniting Space and Artificial Intelligence
Elon Musk’s SpaceX Acquires xAI in Historic Deal Uniting Space and Artificial Intelligence  SoftBank Shares Slide After Arm Earnings Miss Fuels Tech Stock Sell-Off
SoftBank Shares Slide After Arm Earnings Miss Fuels Tech Stock Sell-Off  Merck Raises Growth Outlook, Targets $70 Billion Revenue From New Drugs by Mid-2030s
Merck Raises Growth Outlook, Targets $70 Billion Revenue From New Drugs by Mid-2030s  U.S. Vaccine Policy Shifts Under RFK Jr. Create Uncertainty for Pharma and Investors
U.S. Vaccine Policy Shifts Under RFK Jr. Create Uncertainty for Pharma and Investors  Sam Altman Reaffirms OpenAI’s Long-Term Commitment to NVIDIA Amid Chip Report
Sam Altman Reaffirms OpenAI’s Long-Term Commitment to NVIDIA Amid Chip Report  Sanofi Gains China Approval for Myqorzo and Redemplo, Strengthening Rare Disease Portfolio
Sanofi Gains China Approval for Myqorzo and Redemplo, Strengthening Rare Disease Portfolio  Sanofi to Acquire Dynavax in $2.2 Billion Deal to Strengthen Vaccine Portfolio
Sanofi to Acquire Dynavax in $2.2 Billion Deal to Strengthen Vaccine Portfolio  Jensen Huang Urges Taiwan Suppliers to Boost AI Chip Production Amid Surging Demand
Jensen Huang Urges Taiwan Suppliers to Boost AI Chip Production Amid Surging Demand  Nvidia, ByteDance, and the U.S.-China AI Chip Standoff Over H200 Exports
Nvidia, ByteDance, and the U.S.-China AI Chip Standoff Over H200 Exports  Tencent Shares Slide After WeChat Restricts YuanBao AI Promotional Links
Tencent Shares Slide After WeChat Restricts YuanBao AI Promotional Links  Novo Nordisk Stock Surges After FDA Approves Wegovy Pill for Weight Loss
Novo Nordisk Stock Surges After FDA Approves Wegovy Pill for Weight Loss  SpaceX Updates Starlink Privacy Policy to Allow AI Training as xAI Merger Talks and IPO Loom
SpaceX Updates Starlink Privacy Policy to Allow AI Training as xAI Merger Talks and IPO Loom  California Jury Awards $40 Million in Johnson & Johnson Talc Cancer Lawsuit
California Jury Awards $40 Million in Johnson & Johnson Talc Cancer Lawsuit