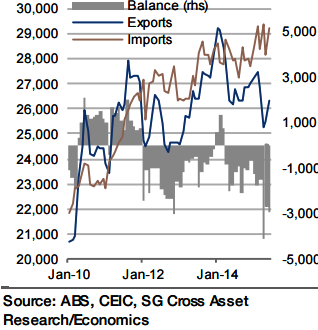
According to the official advanced estimate, imports were practically unchanged in July from June (0.2% mom), meaning that they remained at a high level, and were up by around 4.5% yoy. That said, all of this gain, and more, can be explained by the exchange rate, which in trade-weighted terms was down 13.5% yoy in July.
The volume of imports was estimated about flat over the past year, with the difference explained by weakness in commodity prices, specifically oil, of which Australia is a net importer. Exports, meanwhile, are expected to have continued their recovery after the 8.1% decline they suffered in March/April, but faced a serious headwind in July as the price of iron ore plummeted 17% from June (Port of Qingdao).
"Still, China's July figures for imports from Australia jumped to -4.5% yoy from - 26.5% in June, a move that can only partly be explained by a base effect. Overall, a muted 0.5% increase is expected in exports. As a consequence, the trade deficit should only improve fractionally", says Societe Generale.
Australia's robust imports and weak export prices keep trade deficit elevated
Monday, August 31, 2015 6:09 AM UTC
Editor's Picks
- Market Data
Most Popular



 ADB: Short Strait of Hormuz Closure Would Have Limited Impact on Developing Asia Growth
ADB: Short Strait of Hormuz Closure Would Have Limited Impact on Developing Asia Growth  Trump Offers U.S. Insurance and Naval Escort for Tankers as Strait of Hormuz Crisis Disrupts Global Oil Trade
Trump Offers U.S. Insurance and Naval Escort for Tankers as Strait of Hormuz Crisis Disrupts Global Oil Trade  Oil Tanker Attacks in Gulf Escalate U.S.–Iran Conflict, Driving Energy Prices Higher
Oil Tanker Attacks in Gulf Escalate U.S.–Iran Conflict, Driving Energy Prices Higher  China Sets 2026 Growth Target at 4.5–5% While Prioritizing Innovation and Industrial Strength
China Sets 2026 Growth Target at 4.5–5% While Prioritizing Innovation and Industrial Strength  Australia and Canada Strengthen Critical Minerals Partnership Through New G7 Alliance Agreements
Australia and Canada Strengthen Critical Minerals Partnership Through New G7 Alliance Agreements  China Factory Activity Surges to Five-Year High as Demand Boosts Manufacturing PMI
China Factory Activity Surges to Five-Year High as Demand Boosts Manufacturing PMI  Chinese Yuan Edges Higher but Faces Biggest Weekly Drop in Over a Year Amid Strong Dollar
Chinese Yuan Edges Higher but Faces Biggest Weekly Drop in Over a Year Amid Strong Dollar  Dollar Rally Pauses as Euro Stabilizes Amid Middle East War Uncertainty
Dollar Rally Pauses as Euro Stabilizes Amid Middle East War Uncertainty  Oil Prices Surge to 2025 High as U.S.-Israel Conflict With Iran Threatens Global Energy Supply
Oil Prices Surge to 2025 High as U.S.-Israel Conflict With Iran Threatens Global Energy Supply  European Stocks Slide as Middle East War Fears and Rising Oil Prices Shake Markets
European Stocks Slide as Middle East War Fears and Rising Oil Prices Shake Markets 






























