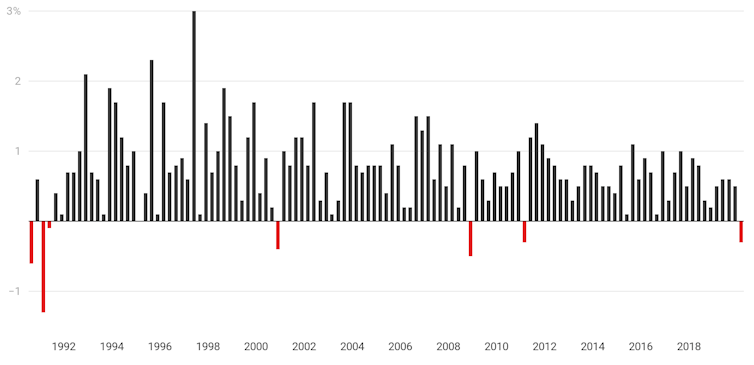
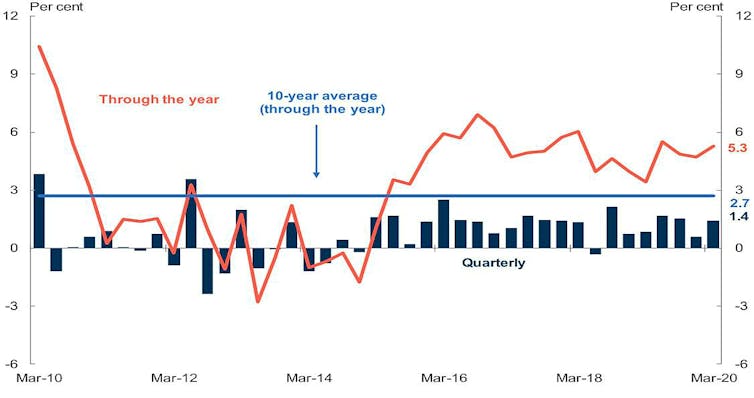
A go-slow on spending sent the economy backwards 0.3% in the first three months of this year, only the fourth such decline since Australia was last in recession in the early 1990s.
Treasurer Josh Frydenberg says treasury has told him that the next three months, the June quarter that we are in at present, will see a “far more severe” contraction, one private sector forecasters believe could be as high as 10%.
Asked whether that meant Australia was already in recession, he said it did.
Quarterly GDP growth since 1990
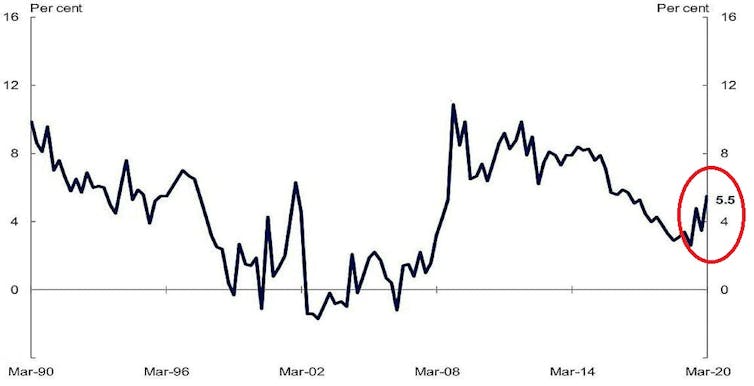
Most unusually for an economic downturn, household incomes rose throughout the quarter, pushed higher by a 6.2% increase in government payments related to COVID-19 and the bushfires, and an 11.1% increase in insurance payouts as a result of bushfires and hailstorms.
But rather than spend most of it, Australian households dramatically increased saving in the quarter, pushing the household saving ratio up from 3.5% to 5.5% and pushing down household spending 0.2%.
Household savings ratio
Commonwealth Treasury
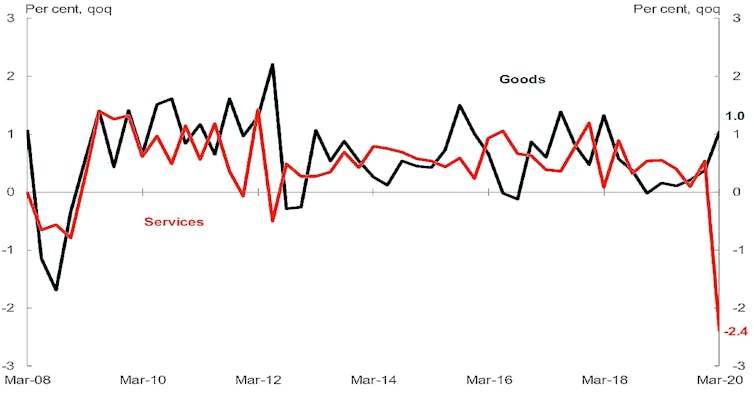
Spending on goods actually increased over the three months as Australians stocked up on essentials including toilet paper in March.
The production of “petroleum, coal, chemical and rubber products” surged 8.1% as consumers stocked up on cleaning and disinfectant products.
But spending on services plummeted, led down by dramatic falls in spending on transport and hotels, cafes and restaurants.
Household consumption, March quarter
Commonwealth Treasury
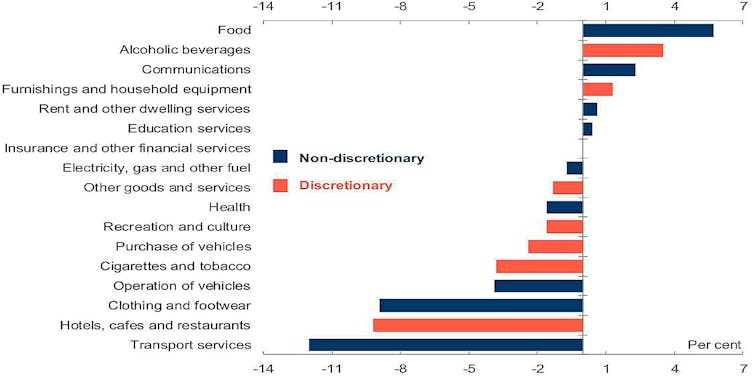
Spending on transport services (airlines and the like) fell 12.0%. Spending on hotels, cafes and restaurants fell 9.2%, each the biggest fall on record.
“Production” in these industries fell 4.9% and 7.5%. Profits fell 6.8% and 14.2%.
Spending fell on ten of the 17 consumption categories.
Household consumption by category, March quarter
Commonwealth Treasury
Most of the changes took place at the very end of the March quarter.
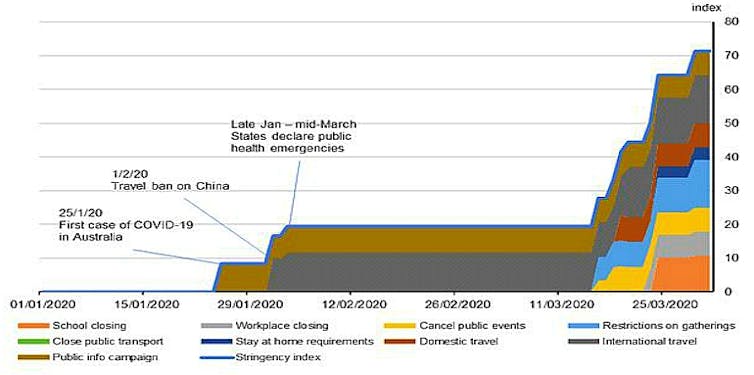
A new index of the “stringency” of COVID-19 containment measures released with the national accounts shows they ramped up only in the final two weeks.
Most have been in place for the entirety of the June quarter to date, suggesting the impacts on spending and production will be a “lot more substantial”, in the words the treasurer used in the national accounts press conference.
ABS stringency of containment measures index
Were it not for government spending, which has climbed 6.2% throughout the year, the plunge in March quarter GDP would have been much more severe.
Calculations of the Bureau of Statistics suggest it would have been twice as severe, a March quarter decline of 0.6% rather than 0.3%.
General government expenditure
Commonwealth Treasury
The treasurer described Australia as “on the edge of the cliff” in the March quarter, facing “an economist’s version of Armageddon”.
The treasury had been contemplating a fall in gross domestic product of 20% in the June quarter. Australia has avoided that fate by acting on health and the economy early.
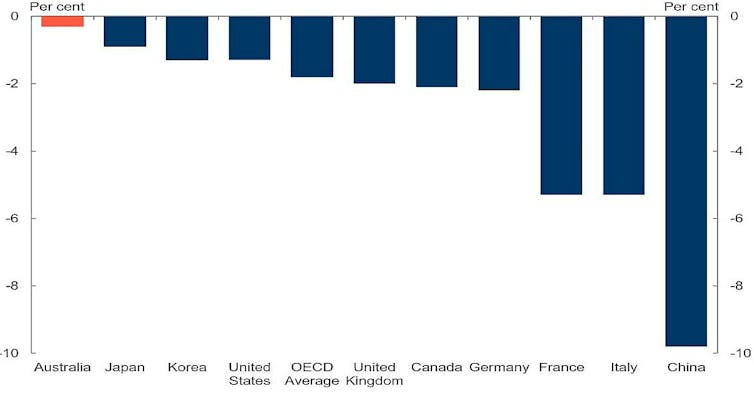
Its fall in GDP of 0.3% in the March quarter was one third the OECD average.
International comparisons, real GDP growth, March quarter
Commonwealth Treasury
The treasurer has scheduled an economic update, which will include the result of a review of the JobKeeper program.
Asked whether it could be referred to as a mini-budget, he said it could be.
Peter Martin ne travaille pas, ne conseille pas, ne possède pas de parts, ne reçoit pas de fonds d'une organisation qui pourrait tirer profit de cet article, et n'a déclaré aucune autre affiliation que son poste universitaire.



 RBI Holds Repo Rate at 5.25% as India’s Growth Outlook Strengthens After U.S. Trade Deal
RBI Holds Repo Rate at 5.25% as India’s Growth Outlook Strengthens After U.S. Trade Deal  Silver Prices Plunge in Asian Trade as Dollar Strength Triggers Fresh Precious Metals Sell-Off
Silver Prices Plunge in Asian Trade as Dollar Strength Triggers Fresh Precious Metals Sell-Off  Trump Endorses Japan’s Sanae Takaichi Ahead of Crucial Election Amid Market and China Tensions
Trump Endorses Japan’s Sanae Takaichi Ahead of Crucial Election Amid Market and China Tensions  Global Markets Slide as AI, Crypto, and Precious Metals Face Heightened Volatility
Global Markets Slide as AI, Crypto, and Precious Metals Face Heightened Volatility  South Africa Eyes ECB Repo Lines as Inflation Eases and Rate Cuts Loom
South Africa Eyes ECB Repo Lines as Inflation Eases and Rate Cuts Loom  Dollar Steadies Ahead of ECB and BoE Decisions as Markets Turn Risk-Off
Dollar Steadies Ahead of ECB and BoE Decisions as Markets Turn Risk-Off  China Extends Gold Buying Streak as Reserves Surge Despite Volatile Prices
China Extends Gold Buying Streak as Reserves Surge Despite Volatile Prices  Trump’s Inflation Claims Clash With Voters’ Cost-of-Living Reality
Trump’s Inflation Claims Clash With Voters’ Cost-of-Living Reality  India–U.S. Interim Trade Pact Cuts Auto Tariffs but Leaves Tesla Out
India–U.S. Interim Trade Pact Cuts Auto Tariffs but Leaves Tesla Out  Dow Hits 50,000 as U.S. Stocks Stage Strong Rebound Amid AI Volatility
Dow Hits 50,000 as U.S. Stocks Stage Strong Rebound Amid AI Volatility  Bank of Japan Signals Readiness for Near-Term Rate Hike as Inflation Nears Target
Bank of Japan Signals Readiness for Near-Term Rate Hike as Inflation Nears Target  Gold and Silver Prices Slide as Dollar Strength and Easing Tensions Weigh on Metals
Gold and Silver Prices Slide as Dollar Strength and Easing Tensions Weigh on Metals  South Korea Assures U.S. on Trade Deal Commitments Amid Tariff Concerns
South Korea Assures U.S. on Trade Deal Commitments Amid Tariff Concerns  Vietnam’s Trade Surplus With US Jumps as Exports Surge and China Imports Hit Record
Vietnam’s Trade Surplus With US Jumps as Exports Surge and China Imports Hit Record  Oil Prices Slide on US-Iran Talks, Dollar Strength and Profit-Taking Pressure
Oil Prices Slide on US-Iran Talks, Dollar Strength and Profit-Taking Pressure  Fed Governor Lisa Cook Warns Inflation Risks Remain as Rates Stay Steady
Fed Governor Lisa Cook Warns Inflation Risks Remain as Rates Stay Steady  Trump Lifts 25% Tariff on Indian Goods in Strategic U.S.–India Trade and Energy Deal
Trump Lifts 25% Tariff on Indian Goods in Strategic U.S.–India Trade and Energy Deal