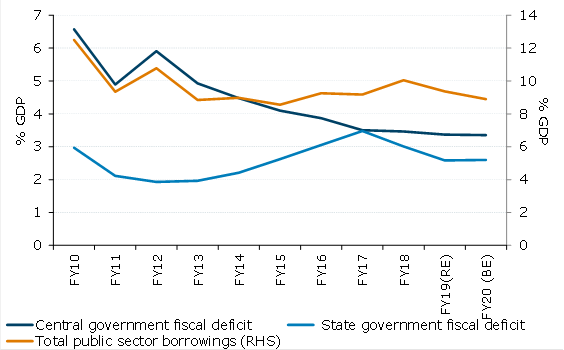
The inability of bond yields to break lower despite an unprecedented scale of liquidity infusion by the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) and expectations of further monetary easing is explained by the worsening fiscal position, according to the latest report from ANZ Research.
The government has now deviated from the fiscal roadmap in four of its five years in tenure. The medium term fiscal deficit target of 3 percent of GDP, initially to be achieved in FY17 (fiscal year ending March 2017) has been pushed out to FY21 (fiscal year ending March 2021).
Higher off-budget funding of public capital spending has also under-stated the real extent of India’s fiscal deficit. The management of the disinvestment process has also shifted from initial public offerings to the public to private placements with state-owned insurance companies and share buybacks by state enterprises, the report added.
At the current run rate, the combined central-state government debt ratio of 60 percent can be attained by the revised timeline of FY25 as laid out in the fiscal roadmap. This is however, sensitive to the underlying assumptions, especially nominal GDP growth.
"The current accommodative fiscal-monetary mix has not filtered through to the currency market as yet. The closure of the output gap, which will also result in a widening of the current account deficit, could well be the inflexion point," ANZ Research further commented.



 Trump Lifts 25% Tariff on Indian Goods in Strategic U.S.–India Trade and Energy Deal
Trump Lifts 25% Tariff on Indian Goods in Strategic U.S.–India Trade and Energy Deal  RBI Holds Repo Rate at 5.25% as India’s Growth Outlook Strengthens After U.S. Trade Deal
RBI Holds Repo Rate at 5.25% as India’s Growth Outlook Strengthens After U.S. Trade Deal  China Extends Gold Buying Streak as Reserves Surge Despite Volatile Prices
China Extends Gold Buying Streak as Reserves Surge Despite Volatile Prices  UK Starting Salaries See Strongest Growth in 18 Months as Hiring Sentiment Improves
UK Starting Salaries See Strongest Growth in 18 Months as Hiring Sentiment Improves  Best Gold Stocks to Buy Now: AABB, GOLD, GDX
Best Gold Stocks to Buy Now: AABB, GOLD, GDX  Gold Prices Fall Amid Rate Jitters; Copper Steady as China Stimulus Eyed
Gold Prices Fall Amid Rate Jitters; Copper Steady as China Stimulus Eyed  Dollar Near Two-Week High as Stock Rout, AI Concerns and Global Events Drive Market Volatility
Dollar Near Two-Week High as Stock Rout, AI Concerns and Global Events Drive Market Volatility  Gold and Silver Prices Rebound After Volatile Week Triggered by Fed Nomination
Gold and Silver Prices Rebound After Volatile Week Triggered by Fed Nomination  Asian Currencies Stay Rangebound as Yen Firms on Intervention Talk
Asian Currencies Stay Rangebound as Yen Firms on Intervention Talk  Trump Signs Executive Order Threatening 25% Tariffs on Countries Trading With Iran
Trump Signs Executive Order Threatening 25% Tariffs on Countries Trading With Iran