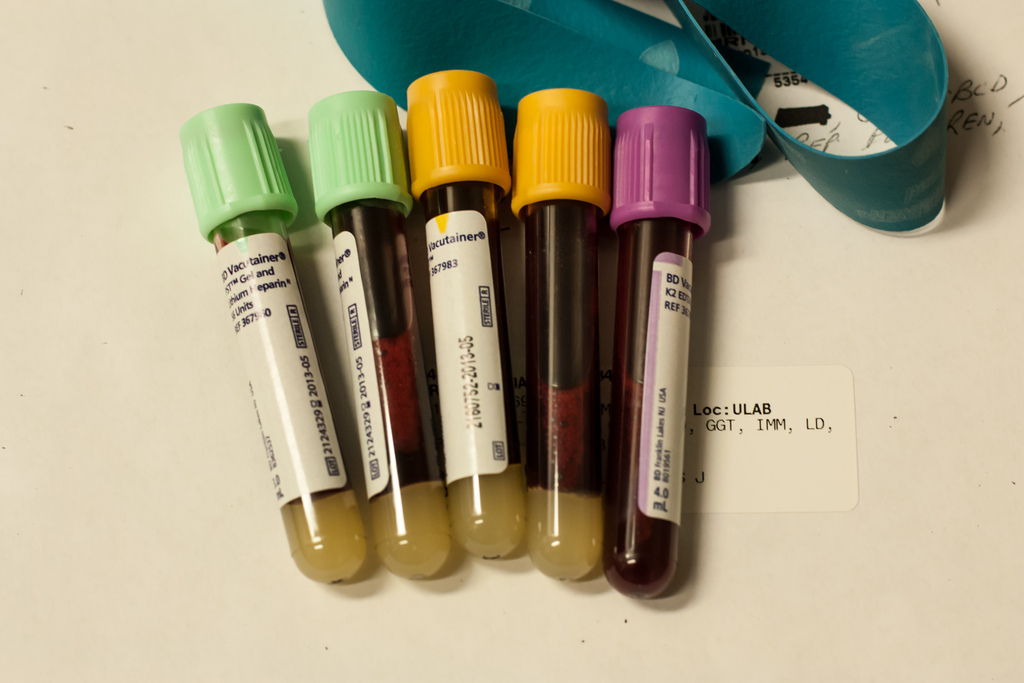
Autism remains one of the biggest mysteries in the medical industry right now, with the root cause still being unidentified. What’s worse is that early detection of the illness has been rather unreliable. This may soon change with two new tests developed by scientists, which make use of blood and urine to determine if a child has autism or not.
The study was done by researchers at the University of Warwick, who built on previous research that find a link between damaged protein found in blood plasma and the occurrence of autism. In the press release talking about the breakthrough, the researchers note how this could vastly improve detection of autism in children.
Leading the study is Dr. Naila Rabbani and according to her, the hope involving these new tests is being able to take the necessary steps for intervention early in the life of the patients with autism. They also hope to one discover the root cause of autism after building on these models.
"We hope the tests will also reveal new causative factors. With further testing, we may reveal specific plasma and urinary profiles or "fingerprints" of compounds with damaging modifications. This may help us improve the diagnosis of ASD and point the way to new causes of ASD," Dr. Rabbani said.
The tests themselves rely on differentiating chemical properties from the subjects using Artificial Intelligence, Futurism notes. The researchers basically took samples from two groups of children, one of which is healthy and the other being composed of patients suffering from autism.
For now, the only thing that current science is able to tell is that the samples are chemically different from each other. As a result, children tested to have the damaged protein are most likely to develop autism. By having subjects as young as toddlers who are two years of age tested, parents become better prepared to deal with the ensuing hardships to follow.



 Trump Signs Executive Order to Boost AI Research in Childhood Cancer
Trump Signs Executive Order to Boost AI Research in Childhood Cancer  Senate Sets December 8 Vote on Trump’s NASA Nominee Jared Isaacman
Senate Sets December 8 Vote on Trump’s NASA Nominee Jared Isaacman  Is space worth the cost? Accounting experts say its value can’t be found in spreadsheets
Is space worth the cost? Accounting experts say its value can’t be found in spreadsheets  FDA Pilot Program Eases Rules for Nicotine Pouch Makers
FDA Pilot Program Eases Rules for Nicotine Pouch Makers  Trump and Merck KGaA Partner to Slash IVF Drug Costs and Expand Fertility Coverage
Trump and Merck KGaA Partner to Slash IVF Drug Costs and Expand Fertility Coverage  Blue Origin’s New Glenn Achieves Breakthrough Success With First NASA Mission
Blue Origin’s New Glenn Achieves Breakthrough Success With First NASA Mission  SpaceX Starship Test Flight Reaches New Heights but Ends in Setback
SpaceX Starship Test Flight Reaches New Heights but Ends in Setback  Trump Administration to Launch Autism Initiatives Targeting Acetaminophen Use and New Treatment Options
Trump Administration to Launch Autism Initiatives Targeting Acetaminophen Use and New Treatment Options  Neuralink Expands Brain Implant Trials with 12 Global Patients
Neuralink Expands Brain Implant Trials with 12 Global Patients  SpaceX Prioritizes Moon Mission Before Mars as Starship Development Accelerates
SpaceX Prioritizes Moon Mission Before Mars as Starship Development Accelerates  Cogent Biosciences Soars 120% on Breakthrough Phase 3 Results for Bezuclastinib in GIST Treatment
Cogent Biosciences Soars 120% on Breakthrough Phase 3 Results for Bezuclastinib in GIST Treatment