The Reserve Bank’s long-awaited two-year forecasts for jobs, wages and growth are frightening, but I fear they are not frightening enough.
The bank looks two years ahead every three months. The last set of forecasts, released at the start of February, mentioned coronavirus mainly as a source of “uncertainty”.
That’s how much things have changed.
Back then economic growth was going to climb over time, consumers were going to start opening their wallets again (household spending had been incredibly weak) and unemployment was going to plunge below 5%.
The forecasts released on Friday come in three sets – “baseline”, a quicker economic recovery, and a slower recovery.
“Baseline”, the central set with which we will concern ourselves here, is both shocking, and disconcertingly encouraging.
Reserve Bank Statement on Monetary Policy, May 2020
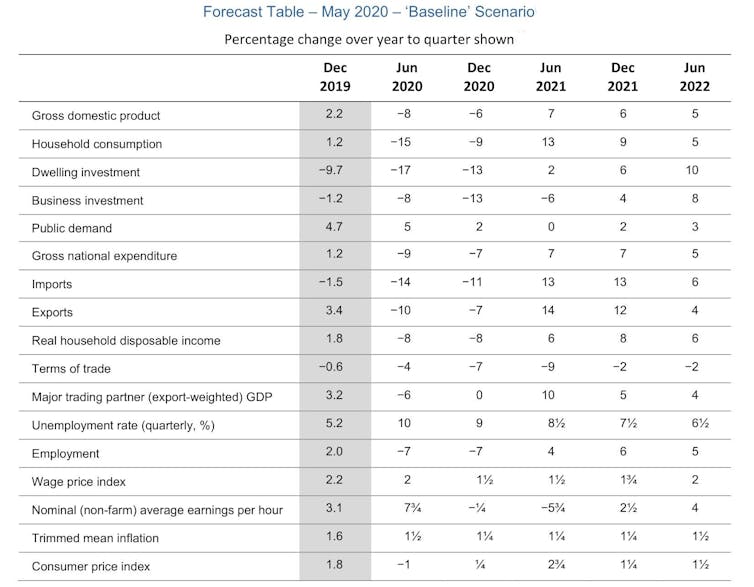
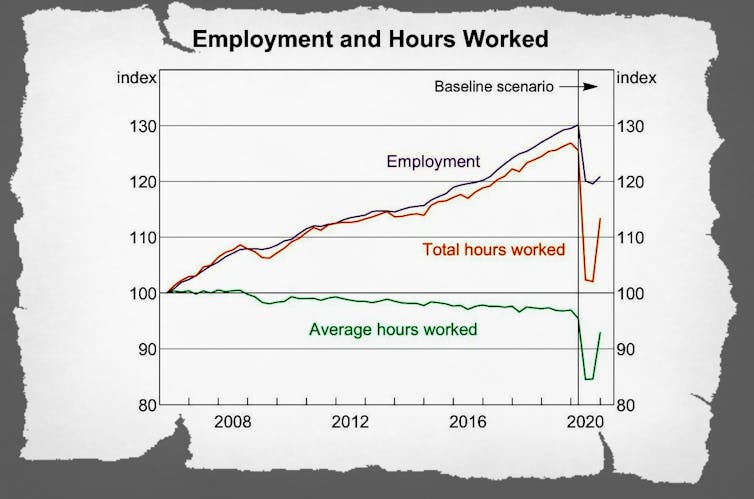
On employment, it predicts a drop of more than 7% in the first half of this year, most of it in the “June quarter”, the three months of April, May and June that we are in the middle of.
Thirteen million of us were employed in March, making a drop of 7%, a drop of 900,000. Put differently, one in every 13 of us will lose their jobs.
Herder to believe is that by December next year 6% of the workforce will have got hem back.
It sounds like what the prime minister referred to earlier in the crisis as a “snapback”, the economy snapping back to where it was.
Except that it’s not.
Reserve Bank Statement on Monetary Policy, May 2020
Six per cent of a small number is a lot less than 7% of a big number.
The bank’s forecasts have far fewer people in work all the way out to mid 2022 (the limit of the published forecasts) and doubless well beyond.
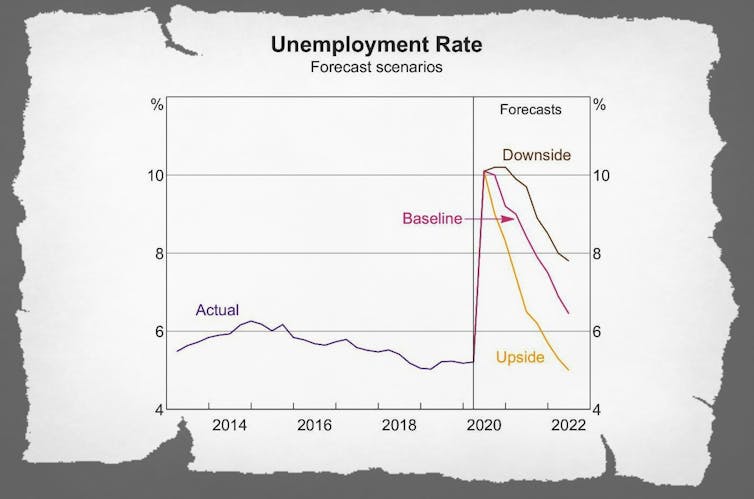
The unemployment rate would shoot up to 10% by June and take a long while to fall.
Reserve Bank Statement on Monetary Policy, May 2020
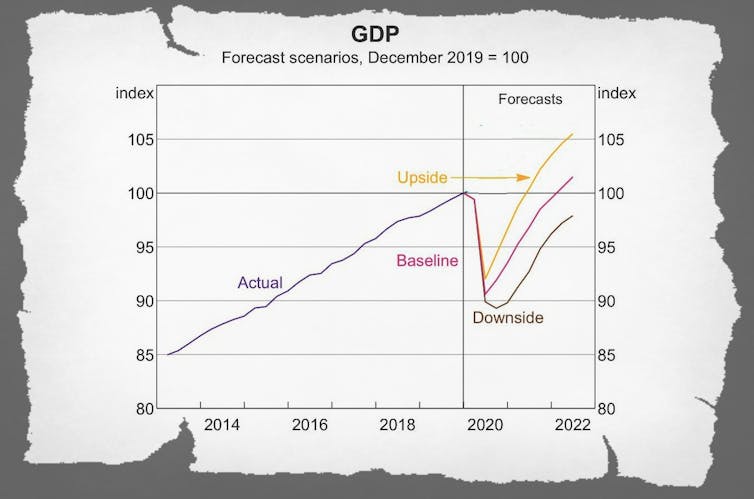
The baseline economic growth forecast is also drawn as a V.
After economic activity shrinks more than 8% in the June quarter, we are asked to believe it will bound back 7% in the year that follows.
But that will still leave us with much lower living standards than we would have had, missing the usual 2-3% per year increase.
Reserve Bank Statement on Monetary Policy, May 2020
The reason I fear the baseline forecasts aren’t frightening enough is that they are partly built on a return to form for household spending, which accounts for 65% of gross domestic product.
After diving 15% mainly in this quarter we are asked to believe it will climb back 13% in the year that follows.
Maybe. But here’s another theory. While we’ve been restricted in movement or without jobs we’ve become used to spending less (and used to flying less, and used to hanging onto our cars for longer and hanging on to the money we’ve got).
My suspicion is that these behaviours can be learned, and we’ve been doing them long enough to learn them.
During the global financial crisis we tightened our belts and then kept them tight for years, saving far more than the offical forecasts expected, in part because we had been shocked and felt certain about the future.
A recovery that had been forecast to be V-shaped looked more like a flat-bottomed boat when graphed. It’s a picture I find more believable than a snapback.
We are unlikley to have been back where we would have been for a very long time.
 Peter Martin does not work for, consult, own shares in or receive funding from any company or organisation that would benefit from this article, and has disclosed no relevant affiliations beyond their academic appointment.
Peter Martin does not work for, consult, own shares in or receive funding from any company or organisation that would benefit from this article, and has disclosed no relevant affiliations beyond their academic appointment.



 South Africa Eyes ECB Repo Lines as Inflation Eases and Rate Cuts Loom
South Africa Eyes ECB Repo Lines as Inflation Eases and Rate Cuts Loom  U.S. Stock Futures Slide as Tech Rout Deepens on Amazon Capex Shock
U.S. Stock Futures Slide as Tech Rout Deepens on Amazon Capex Shock  Global Markets Slide as AI, Crypto, and Precious Metals Face Heightened Volatility
Global Markets Slide as AI, Crypto, and Precious Metals Face Heightened Volatility  RBA Expected to Raise Interest Rates by 25 Basis Points in February, ANZ Forecast Says
RBA Expected to Raise Interest Rates by 25 Basis Points in February, ANZ Forecast Says  South Korea Assures U.S. on Trade Deal Commitments Amid Tariff Concerns
South Korea Assures U.S. on Trade Deal Commitments Amid Tariff Concerns  Trump Endorses Japan’s Sanae Takaichi Ahead of Crucial Election Amid Market and China Tensions
Trump Endorses Japan’s Sanae Takaichi Ahead of Crucial Election Amid Market and China Tensions  Bank of Japan Signals Readiness for Near-Term Rate Hike as Inflation Nears Target
Bank of Japan Signals Readiness for Near-Term Rate Hike as Inflation Nears Target  Fed Governor Lisa Cook Warns Inflation Risks Remain as Rates Stay Steady
Fed Governor Lisa Cook Warns Inflation Risks Remain as Rates Stay Steady  Japan Economy Poised for Q4 2025 Growth as Investment and Consumption Hold Firm
Japan Economy Poised for Q4 2025 Growth as Investment and Consumption Hold Firm  Dollar Near Two-Week High as Stock Rout, AI Concerns and Global Events Drive Market Volatility
Dollar Near Two-Week High as Stock Rout, AI Concerns and Global Events Drive Market Volatility  Fed Confirms Rate Meeting Schedule Despite Severe Winter Storm in Washington D.C.
Fed Confirms Rate Meeting Schedule Despite Severe Winter Storm in Washington D.C.  RBI Holds Repo Rate at 5.25% as India’s Growth Outlook Strengthens After U.S. Trade Deal
RBI Holds Repo Rate at 5.25% as India’s Growth Outlook Strengthens After U.S. Trade Deal  Silver Prices Plunge in Asian Trade as Dollar Strength Triggers Fresh Precious Metals Sell-Off
Silver Prices Plunge in Asian Trade as Dollar Strength Triggers Fresh Precious Metals Sell-Off  India–U.S. Interim Trade Pact Cuts Auto Tariffs but Leaves Tesla Out
India–U.S. Interim Trade Pact Cuts Auto Tariffs but Leaves Tesla Out  ECB’s Cipollone Backs Digital Euro as Europe Pushes for Payment System Independence
ECB’s Cipollone Backs Digital Euro as Europe Pushes for Payment System Independence